You know that data is a crucial asset for your organization, and you rely on it to drive decisions and strategies. However, data lineage challenges are often unavoidable—
Table of Contents
- Are your data sources standardized?
- Is your metadata accurate?
- How do you ensure compliance with regulations?
These questions highlight the complexities of managing data effectively.
Data lineage, defined as the process of tracking the flow of data from its origin to its final destination, plays a vital role in understanding how data moves and transforms within your systems. To reap the benefits of improved data quality, enhanced compliance, and better decision-making, you must be willing to resolve the data lineage challenges.
In this article, we will explore these challenges in detail and discuss effective strategies for overcoming them, ensuring that your organization can harness the full potential of its data assets.
What is Data Lineage?
Your organizations face numerous challenges without a clear understanding of their data systems. Issues such as data inaccuracies, compliance risks, and inefficient decision-making arise when businesses lack visibility into the flow and transformation of their data. This is where data lineage becomes essential.
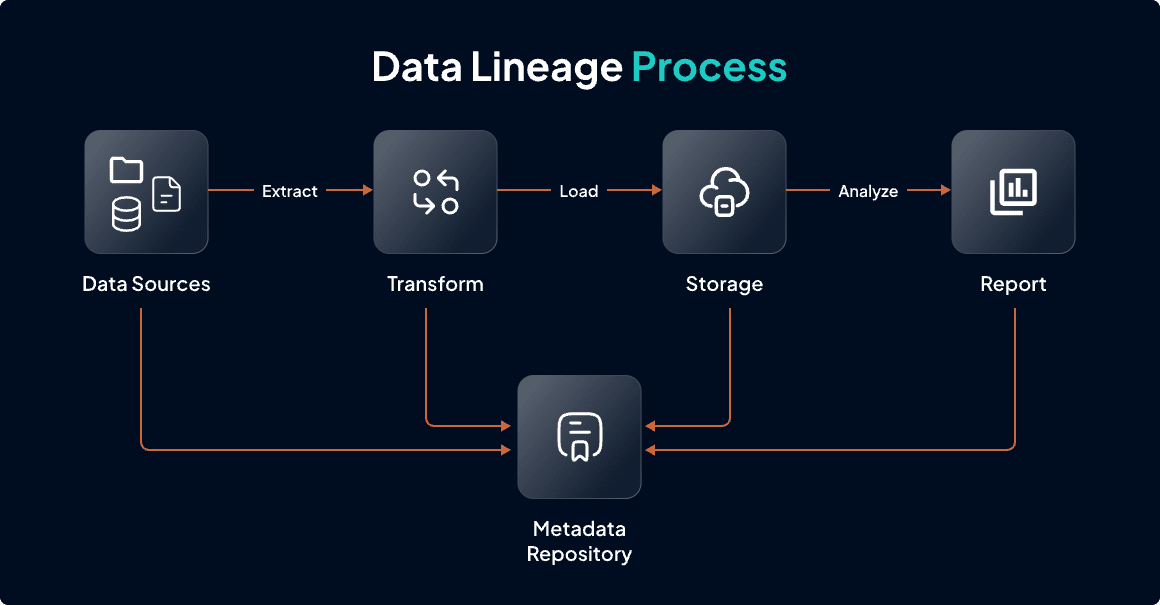
Data lineage refers to the process of tracking the flow of data from its origin through various transformations to its final destination. It provides a comprehensive view of how data moves and changes over time, enabling organizations to ensure data accuracy and reliability. For example, in a retail business, data lineage can illustrate how sales data is collected from point-of-sale systems, processed through analytics platforms, and ultimately reported for financial assessments. Read how to implement data lineage to ensure data accuracy.
Benefits of Data Lineage
- Improved Data Governance: Data lineage shows where data comes from and how it’s changed, helping organizations keep data quality high.
- Increased Data Quality: By seeing the data’s journey, organizations can find and fix errors, improving data quality.
- Faster Impact Analysis: If something changes in one part of the system, data lineage helps see the impact on other areas quickly, helping fast decision-making and minimizing issues.
- Improved Compliance: Tracking data flows helps organizations meet regulatory requirements, ensuring transparency and accountability in data practices.
- Contextual Understanding: Data lineage provides context, helping teams make decisions based on accurate information.
Pro Tip: To maximize the benefits of data lineage, regularly update your lineage documentation and invest in automated tools that streamline lineage tracking. This proactive approach will enhance your organization’s ability to manage and leverage its data effectively.-
What Are the Key Challenges in Implementing Data Lineage?
While data lineage helps improve data quality, compliance, and decision-making, setting up these systems or migrating data can be challenging, as it may introduce errors or complexities.
Below we discuss some key data lineage challenges you could face:
1. Lack of Standardization in Data Sources
Data can come from various places, each with its own format and naming system. This makes it hard to track and manage data lineage properly, leading to errors and issues when combining data from different sources becoming one of the major data lineage challenges.
How can this happen?
When a company uses multiple systems like databases or cloud services, each might handle data differently, causing inconsistencies. For example, one department might use a specific format for customer IDs, while another uses a different one, making it hard to track the history of customer data.
2. Incomplete or Inaccurate Metadata
Metadata is essential for understanding data lineage. If it’s incomplete or inaccurate, it can lead to confusion about where data comes from and how it’s been changed. Inconsistencies in reports or unexpected results during data analysis can indicate issues with metadata.
How can this happen?
When data is moved without proper documentation or when changes are made without updating the metadata. For example, if a dataset lacks descriptions of how values were calculated, users might misinterpret the data’s meaning.
3. Scalability Issues with Large-Scale Data Systems
As organizations grow, their data volume increases, making it hard to maintain effective lineage tracking across large datasets. Performance issues or slow response times when querying lineage information can indicate scalability problems.
How can this happen?
Large-scale systems often have numerous interconnected parts, making it complicated to track data flows. For example, an e-commerce platform experiencing rapid growth may find it hard to track customer interactions across multiple channels efficiently.
4. Limited Automation in Lineage Tracking
Manual tracking of data lineage is time-consuming and prone to errors. Limited automation can hurt efficiency and accuracy, requiring frequent manual updates and corrections.
How can this happen?
Organizations might use outdated tools that lack automated tracking features. For example, if a company updates its data lineage manually every month, they could miss real-time changes, leading to outdated information.
5. Regulatory and Compliance Complexities
Organizations need to follow various rules and laws about data handling, which can complicate lineage tracking. Increased scrutiny from regulators or compliance audits might reveal gaps in data lineage processes.
How can this happen?
Different regions have different laws (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), making it tough to maintain compliance across all datasets. For example, a healthcare provider must ensure patient data is tracked accurately to comply with HIPAA regulations, adding complexity to their lineage efforts.
6. Cost of Implementing Data Lineage Solutions
Implementing comprehensive data lineage solutions often requires significant investment in tools and resources. Budget overruns or resource shortages during implementation phases can indicate financial challenges.
How can this happen?
Costs can escalate due to the need for specialized software, training personnel, and ongoing maintenance. For example, a small business might struggle to afford the advanced lineage tools that larger competitors use effectively.
7. Poor Collaboration Across Teams
Data lineage needs input from various teams (e.g., IT, compliance, business units). Poor collaboration can lead to fragmented understanding and execution of lineage processes. Conflicts in data management practices or inconsistent reporting across departments can signal collaboration issues.
How can this happen?
Siloed departments may not communicate effectively about data handling practices or changes. For example, if marketing and sales teams use different metrics for customer engagement without aligning on definitions, tracking overall customer behavior becomes difficult.
Solutions to Overcome Data Lineage Challenges
Now that we’ve explored how data lineage challenges can disrupt data management capabilities, we’ll dive into solutions to overcome these obstacles and help your organization make better decisions.
1. Leverage Modern Data Lineage Tools
Many organizations use old tools that can’t keep up with their data needs.
Solution: Investing in modern data lineage tools can automate tracking and provide real-time insights into data flows. These tools often have user-friendly interfaces and features that make it easier to understand data origins and changes.
2. Invest in Metadata Management
Incomplete or inaccurate metadata can lead to confusion about data usage and lineage.
Solution: Implementing a strong metadata management strategy ensures that all data is well-documented and easy to access. Regular updates and audits of metadata maintain its accuracy, helping teams understand the context and lineage of their data.
3. Foster Collaboration Across Stakeholders
Poor communication between departments creates silos, making it hard to track data lineage effectively.
Solution: Encouraging regular meetings and open communication among teams—such as IT, compliance, and business units—can enhance collaboration. Using shared platforms for documentation and updates ensures everyone is on the same page regarding data practices.
4. Adopt a Scalable and Flexible Data Architecture
As organizations grow, their existing data systems may not support increased complexity or volume.
Solution: Designing scalable data architecture allows for easy integration of new data sources and systems. This flexibility ensures your data lineage processes can adapt as your organization evolves without significant overhauls.
5. Focus on Compliance as a Priority
Regulatory requirements can be overwhelming, leading to gaps in compliance tracking.
Solution: Making compliance a core focus involves regularly reviewing regulations relevant to your industry and ensuring that your data lineage processes align with these requirements. Training staff on compliance issues helps maintain awareness and accountability across the organization.
Real-World Examples of Overcoming Data Lineage Challenges
Case Study 1: Panasonic in the Technology Sector
Problem: Panasonic’s Smart Mobility Office faced significant challenges with data discovery and governance due to the massive volume of connected data, exceeding 3TB weekly. This complexity made it difficult to manage data lineage effectively.
How they tackled lineage issues: To address these challenges, Panasonic partnered with Secoda to implement a centralized documentation tool. This modern data lineage solution streamlined the tracking of data flows and enhanced transparency across departments, allowing teams to trust the data they used.
Key Takeaways:
- Centralized documentation improves data discoverability.
- Trust in data usage is essential for effective decision-making.
- Modern tools can simplify complex data environments.
Case Study 2: Air France in the Aviation Industry
Problem: Air France encountered difficulties with processing and segregating vast amounts of data from over 2.5 million new website visitors daily. This complexity hindered their ability to deliver personalized services without breaching GDPR regulations.
How they tackled lineage issues: The airline collaborated with Talend to develop a robust data lineage system that enabled their data scientists to track and manage customer interactions effectively. This solution facilitated real-time updates and personalized advertising while ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Key Takeaways:
- Effective data lineage supports compliance with regulations.
- Real-time updates enhance customer engagement.
- Collaboration with specialized partners can streamline complex data management.
Conclusion
In summary, to optimize your organization’s data management practices, understanding data lineage is key. Data lineage refers to the ability to track and visualize the flow of data throughout its lifecycle. Be it improving data quality, ensuring regulatory compliance, or enhancing operational efficiency, the importance of addressing data lineage challenges cannot be overstated.
However, with a focus on leveraging modern tools, investing in metadata management, and fostering collaboration across teams, you can effectively tackle these data lineage challenges. While you now know you are prepared to face these issues, having support to guide you through the unique data lineage challenges specific to your business requirements is crucial.
Hevo’s professional experts can provide guidance and tools that support you on your data management journey. What are you waiting for? Sign up for free today!
FAQs
1. What are the risks of data lineage?
Neglecting data lineage leads to significant risks such as data integrity issues, compliance failures, and flawed decision-making. Without a clear record of data origins and transformations, organizations are susceptible to face challenges like data loss, duplication, and corruption. These issues hinder operational efficiency and result in non-compliance with regulations, potentially leading to legal penalties and reputational damage.
2. What are the two types of data lineages?
The two primary types of data lineage are business lineage and technical lineage. Business lineage focuses on the flow of data from a business perspective, illustrating how data is used in processes and decision-making. Technical lineage, on the other hand, provides a detailed view of the data’s journey through systems, including transformations and storage locations.
3. What is an example of a data lineage?
One such example of data lineage can be seen in a financial institution tracking customer transaction data. The lineage would illustrate how data is collected from user inputs, processed through various systems for fraud detection, stored in databases, and eventually reported for compliance audits. This traceability ensures that any discrepancies can be traced back to their source for resolution.



